25 Tips for Optimizing Python Performance

- Understanding Python Performance Optimization
-
25 Ways to Speed Up Python Code
- 1. Embrace Django
- 2. Use PyPy Instead of CPython
- 3. Use NumPy Arrays Instead of Lists
- 4. Use the Built-in “timeit” Module
- 5. Apply Generator Expressions Instead of List Comprehensions
- 6. Use Multiprocessing in Python Coding
- 7. Apply Python Profiling
- 8. Optimize Loops with Code Maps
- 9. Eliminate the Dead Code
- 10. Use Application Monitoring Tools
- 11. Rely on the Peephole Optimization Technique
- 12. Intern Strings in Python
- 13. Use <cProfile> for Profiling
- 14. Use Generators and Keys for Sorting
- 15. Focus on Using Built-in Operators
- 16. Use External Libraries
- 17. Avoid Using Globals
- 18. Use Proper Data Structure
- 19. Apply Multiple Assignments
- 20. Concatenate Strings with Join
- 21. Use 1 for Infinity Loops
- 22. Use Special Libraries to Process Large Datasets
- 23. Use List Comprehension
- 24. Use the Library Function
- 25. Do Not Use .dot Operation
- Summary
- FAQ
We at SoftFormance adore Python. Actually, it is our favorite programming language, as both startups and established enterprises can benefit from Python software development. With its remarkable diversity of libraries and frameworks, Python provides excellent solutions for mobile and web application development.
Over 10+ years in the market, the SoftFormance team has developed and released more than 100 applications using Python and our favorite framework, Django.
We certainly know how to take the maximum out of Python, and we are eager to share our expertise in Python code optimization with you.
Keep reading if you want a development team that knows how to speed up Python code and save your time, money, and effort.
Understanding Python Performance Optimization
To begin with, let’s outline some Python essentials.
One of the main distinctions and selling points of Python is that it is an interpreted language. Python code can be executed directly, eliminating the need for pre-compilation into machine code. This significantly boosts the speed of Python development.
However, Python code needs to undergo interpretation each time it is executed on the processor. To prevent the necessity of recompiling the code with each run, Python employs compiled .pyc files. These files enable the storage of bytecode produced from the original Python code, facilitating caching. Later on, we will dwell on some useful tips on Python code compiling.
Finally, Python code is dynamically typed. This means that you aren’t required to specify a data type every time you create a variable. This dynamic approach significantly boosts the speed of coding with Python, but it can also negatively impact Python’s performance if not managed properly.
Fortunately, this article will give you useful tips on how to speed up Python code and the overall performance of this programming language.
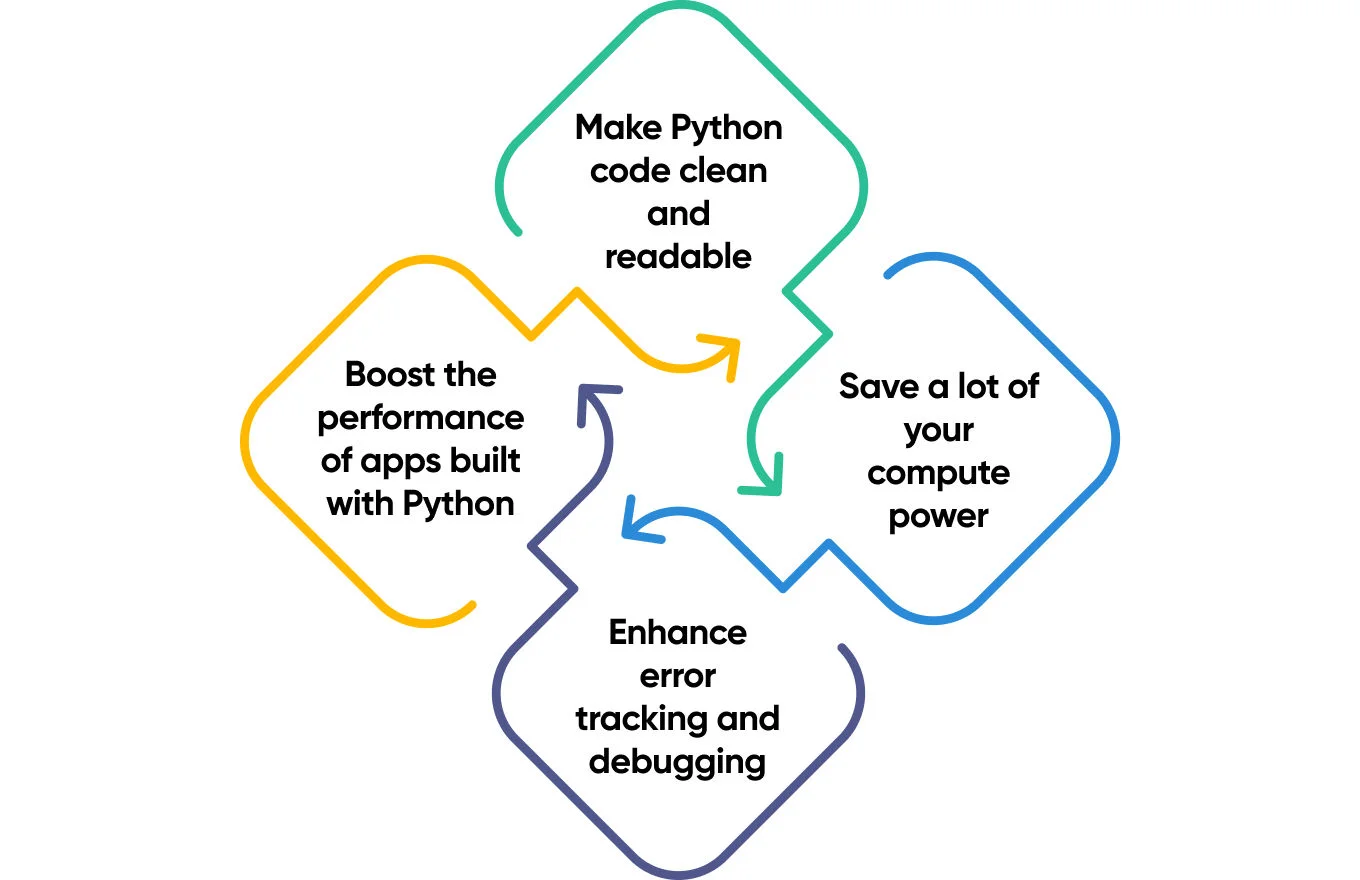
With Python code optimization tips mentioned in this article, you will have great ideas on how to:
- Make Python code clean and readable
- Boost the performance of apps built with Python
- Enhance error tracking and debugging
- Save a lot of your compute power.
So, let’s proceed with…
25 Ways to Speed Up Python Code
As a team that has an impressive track record of successful Python application development projects, we certainly have some advice to offer to Python developers.
Many tips on this list are rather simple yet often overlooked. And, most probably, you will find, at least, some useful ideas here.
1. Embrace Django
Here’s a more general suggestion that will help you embrace the complete potential of Python.
From our experience, there’s no better Python framework than Django.
It is fast, efficient, popular, and rich with Python development tools.
As a result, writing Python code with Django may become a clear highway to success.
But, surely, there are more specific ideas on optimizing Python code to come.
2. Use PyPy Instead of CPython
PyPy is an implementation of Python that uses just-in-time compilation instead of ahead-of-time compilation, peculiar to this language.
As a result, PyPy allows our developers to speed up code execution.
Sometimes, code execution with PyPy can be seven times faster than with CPython.
3. Use NumPy Arrays Instead of Lists
The NumPy library has a great implementation in scientific computing. When dealing with substantial data and mathematical operations, NumPy arrays can significantly outpace common Python lists.
NumPy arrays are tailored for numerical tasks, enhancing efficiency with sizable datasets and consuming less memory than lists. This, in turn, means improved performance.
4. Use the Built-in “timeit” Module
The “timeit” module is a special feature that allows you to control Python, improve performance, and track its efficiency much better.
It allows the developer to measure how long it takes to execute a piece of code.
As a result, there appears a great space for testing the efficiency of different coding approaches.
5. Apply Generator Expressions Instead of List Comprehensions
Generator expressions offer a memory-efficient approach to crafting lists by generating values on-the-fly instead of storing the entire list at once.
Unlike list comprehensions, generator expressions rely on parentheses, yielding a generator object rather than a list, which helps users enhance code performance while minimizing memory consumption.
6. Use Multiprocessing in Python Coding
Multiprocessing allows you to partition your code into multiple processes.
As a result, you can harness the additional processing capability offered by multicore processors, thereby enhancing your code’s performance.
Mind that your technical team may need to show a lot of skill in order to handle multiprocessing properly.
7. Apply Python Profiling
The Python profiling feature is a perfect way for you to track memory usage, measure the number of function calls, and analyze the time needed for the execution of those calls.
Various continuous profilers provided by the vibrant community of Python developers can come in handy.
Or you may aim for a more custom profiler, which will allow you to ensure an always-on approach.
8. Optimize Loops with Code Maps
Loops are very common in coding, and Python provides inherent mechanisms to facilitate them. The point is that such loops often slow down Python programs.
Fortunately, code mapping is here to optimize time utilization and accelerate the execution of such loops.
Code maps are native structure elements that simplify intricate code, making it more shareable and comprehensible. The more efficient and consolidated the code, the better your Python code speed up.
9. Eliminate the Dead Code
While writing Python code, the developers should review it regularly. The point is to remove unnecessary code parts and save memory.
There are multiple ways for removing dead code. These include multiprocessing, using content managers, and relying on preload managers.
10. Use Application Monitoring Tools
Don’t forget to monitor the performance of your Python apps because this allows you to properly evaluate the efficiency of your work.
APM tools, such as New Relic, will come in handy. They benchmark a program, identify performance bottlenecks, and provide optimization solutions to these issues.
11. Rely on the Peephole Optimization Technique
Peephole optimization is a Python coding technique that boosts code performance during the compilation.
Its main tasks are pre-computing constant expressions and employing membership tests.
For example, a developer can improve code readability by writing “a = 606024” to represent the number of seconds in a day. However, the language interpreter automatically calculates this and replaces repetitive instances, which, in turn, boosts software performance.
If you are using Peephole optimization, Python precomputes constant expressions like 606024 and replaces them with the result, such as 86400. This allows you to avoid performance decrease.
12. Intern Strings in Python
Python string objects are sequences of Unicode characters, referred to as “text” sequences in the documentation.
If different character sizes are appended to a string, the overall size and weight of the string grow exponentially. In addition, Python allocates additional information for storing these strings. As a result, too much space is consumed.
That’s when string interning comes into action. It is based on caching of specific strings in memory upon creation.
As a result, only a single instance of each unique string remains active at any point. This, in turn, means more efficient memory allocation.
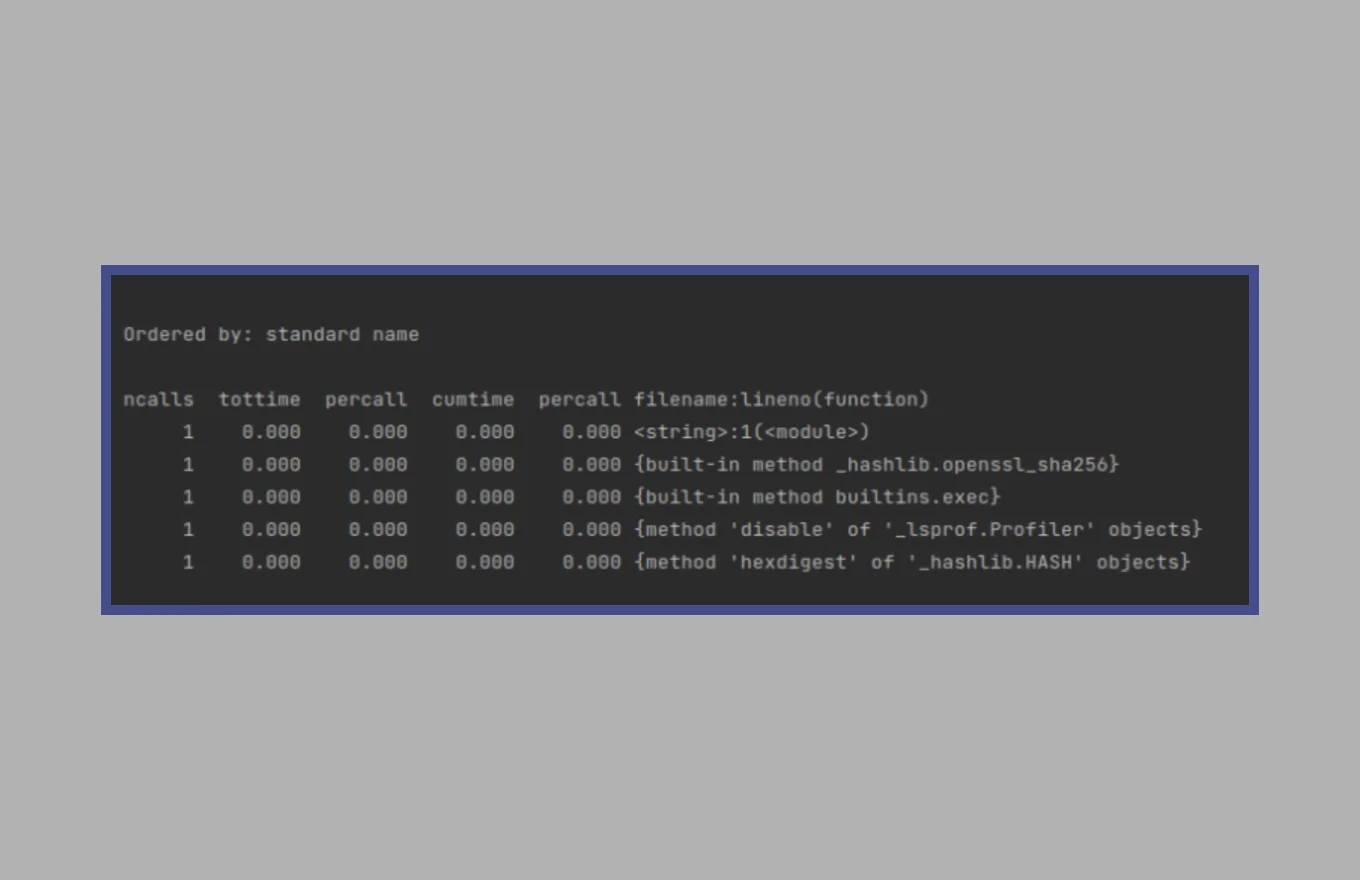
13. Use <cProfile> for Profiling
cProfile offers functionality for advanced profiling, which is part of the Python package since Python 2.5.
You can connect it to the Python code in the following ways:
- Encapsulate a function within its “run” method to measure its performance.;
- Run the command line script, activate cProfile as an argument, and use Python’s “-m” option.
14. Use Generators and Keys for Sorting
Using generators is one more way to optimize memory consumption.
These generators can yield items one by one instead of yielding them all at once. When you are sorting items in a list afterwards, we advise you to employ keys and the default <sort()> method.
The developers can employ this technique to sort both lists and strings based on a chosen index specified within the key argument.
15. Focus on Using Built-in Operators
Python offers a wide array of built-in operators and libraries. We don’t know all of them, but we do know for sure that there are thousands in existence.
Use these built-ins whenever feasible to make your code more efficient. As long as such built-in operators are pre-compiled, they bring you truly swift performance.
16. Use External Libraries
The “C” counterparts of certain Python libraries can bring you the same or even more advanced functionality than the original versions of these libraries. Unsurprisingly, their usage can help you with Python performance optimization.
For example, you may consider substituting Pickle with cPickle to observe the performance disparity.
The developers can also boost Python coding efficiency with the above-mentioned PyPy and <Cython>.
Both these solutions serve as means to optimize a static compiler.
17. Avoid Using Globals
Global variables have their benefits, but they can also bring unexpected side effects, such as excessively complex code structures.
Python performance may drop when you are accessing external variables. So, we advise you to minimize their usage or avoid applying such variables at all.
If there is no way to avoid using globals, consider the following suggestions:
- Apply the ‘global’ keyword to explicitly declare an external variable.
- Before applying globals within loops, generate local copies to boost efficiency.
18. Use Proper Data Structure
Python offers list, tuple, set, and dictionary as the built-in data structures.
And most developers rely on a list of all cases.
However, if you want a truly good performance, check how different data structures fit different cases. And, as a result of your research, choose data structures depending on your needs
19. Apply Multiple Assignments
This approach optimizes and speeds up the code execution.
The key point is to reject variables like this:
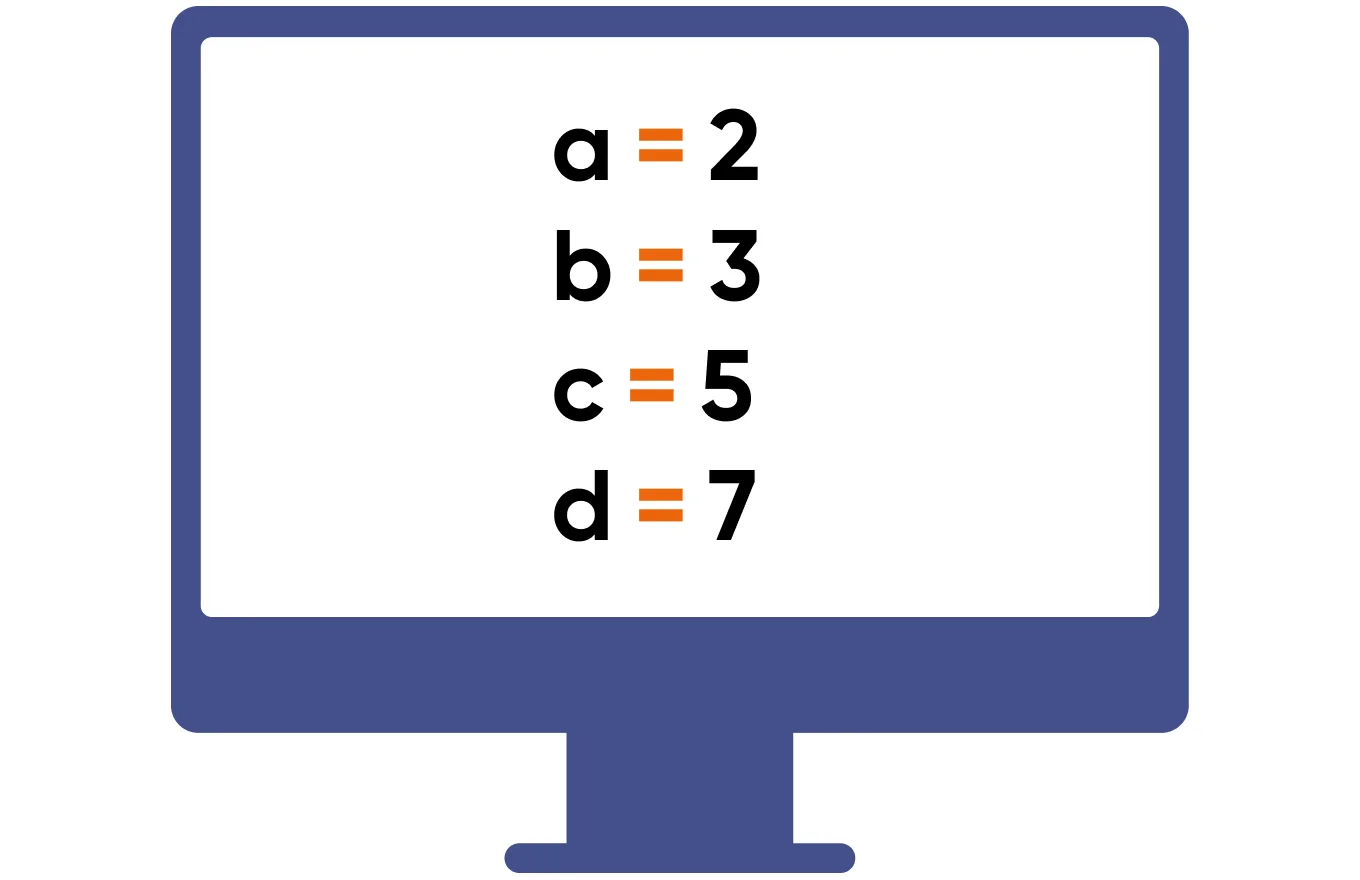
And to assign variables like this:

20. Concatenate Strings with Join
In Python, you have the option to concatenate strings using the + operator. For example:

We recommend you try the join () method because it is faster.
In this case, your optimization code in Python will look the following way:
![concatenatedString = " ".join (["Hello", "world."])](webp/1.6-concatenate-strings-with-join-in-this-case-your-optimization-code-in-python-will-look-the-following-way.webp)
21. Use 1 for Infinity Loops
Instead of using the “while True” construct in your code, rely on the “while 1” construct. Unless quite simple, this modification can reduce your code’s runtime.
The point is that “while 1” offers a more straightforward depiction of an infinite loop condition. This can enhance performance compared to “while True” construct, which is slightly more abstract.
22. Use Special Libraries to Process Large Datasets
C/C++ outperforms Python in terms of speed. And there are numerous packages and modules developed in C/C++ that can be integrated into your Python programs.
Notably, Numpy, Scipy, and Pandas are three prominent examples, known for their effectiveness in handling large datasets.
23. Use List Comprehension
List comprehension is a perfect Python coding practice.
Take a look at an example. What you see is a code to list all the numbers between 1 and 1000 that is the multiplier of 3:
![L = []
for i in range (1, 1000):
if i%3 == 0:
L.append (i)](webp/1.7-use-list-comprehension-what-you-see-is-a-code-to-list-all-the-numbers-between-1-and-1000-that-is-the-multiplier-of-3.webp)
With list comprehension, this code will look as follows:
![L = [i for i in range (1, 1000) if i%3 == 0]](webp/1.8-use-list-comprehension-with-list-comprehension-this-code-will-look-as-follows.webp)
The main benefit of list comprehension is that it can help you improve Python performance.
24. Use the Library Function
Do not write a function that already exists in the library manually.
Library functions prove to be very efficient. Actually, replicating their level of efficiency in your own code can be quite challenging.
And, surely, their use helps you save a lot of time.
25. Do Not Use .dot Operation
Try to avoid dot operations, as it may be time-consuming. Take a look at the example below:

You may write the same operation in the following style:

The point is that the function with a .(dot) first calls __getattribute()__ or __getattr()__, which then uses a dictionary operation. This means that your operation takes more time. We recommend you use the module import function for optimizing Python code for speed.
Summary
So, these 25 tips will help you or your developers optimize the Python code.
As a result, you will develop apps that show excellent performance a few times faster.
But it is always better to rely on specialists who have already mastered these tips long before and know how to improve Python performance.
If you have issues with performance of your Python/Django app, SoftFormance, a perfect Python development team, is ready to help you.
We will thoroughly analyze your code and tune it up with the best Python code optimization techniques.
Contact us to get your Python apps running faster and more efficiently than ever!
FAQ
Generally, Python performance is slower than in compiled languages like C++ or Java, but Python is simpler to use and excels in rapid development.
Some of the techniques for improving Python code performance include concatenating strings with join, applying multiple assignments, using generators as keys for sorting, interning strings, and using the built-in “timeit” module.
To improve Python code performance, you should choose data structures that correspond to your particular tasks and needs.
By speeding up your Python code, you make it more clean and readable, boost the performance of apps built with Python, enhance error tracking and debugging, save a lot of your compute power.
Hi there all, here every person is sharing these kinds of experience, therefore it’s good to read this website, and I used to go to see this webpage all
the time.
Great insights. Helpful. However, I tend to frown upon numbers 19 and 25 in large projects.
Yes, every item counts!
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any issues with hackers?
My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing a few months of hard work due to no data backup.
Do you have any solutions to stop hackers?
Yes, we use cloudflare + ip tables as firewall. works fine