Optimizing Laboratories, CROs and Chemicals R&D Process with Artificial Intelligence

These days, laboratories, Contract Research Organizations (CROs), and Chemical R&D processes drive the revolution in the field of science. Scientists strive to find new ways of streamlining processes and improving productivity, and AI is one of the main solutions that help them achieve these goals.
Unfortunately, traditional methods of research are outdated and face multiple challenges, so AI is a breath of fresh air for laboratories and CROs. AI helps researchers analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make predictions. It also empowers scientists to navigate the complex world of R&D and make more informed decisions easier.
In this article, you’ll learn about what is AI in chemistry, AI chemistry applications, challenges, and limitations, as well as its future prospects.
Applications of AI in Chemistry
AI and ML have a lot of uses in chemical manufacturing. These solutions help automate data extraction, supply chain planning, and quality testing.
Since computer processing capacity is constantly growing, open-source ML frameworks and AI algorithms are used by scientists to revolutionize the way they handle tasks and work with treatments, chemicals, and drugs.
Let’s focus on the main applications of AI in chemistry:
- Detection of Molecular Properties: AI algorithms can analyze chemical data to predict and classify various molecular properties, such as toxicity, solubility, and reactivity. This makes the process of detection faster and less prone to errors, unlike manual detection. Moreover, AI allows scientists to evaluate the potential of a hypothetical molecule.
- Designing Molecules: AI can assist in designing novel molecules with desired properties by generating virtual compound libraries and optimizing molecular structures through iterative algorithms. The use of AI in this field allows the making of revolutionary discoveries in chemical synthesis.
- Discovering Drugs: AI-driven drug discovery platforms can analyze vast databases of chemical compounds, predict their potential activity against specific targets, and prioritize candidates for further investigation. Scientists are now using AI to formulate new effective medicines for curing fatal diseases.
- Retrosynthesis Reaction: Chemists use AI for planning the most efficient and cost-effective synthesis routes by generating retrosynthesis pathways and suggesting optimal reaction steps. This process was conducted manually in the past, which took a lot of time, effort, and money.
- Predictive Analysis: With the use of AI algorithms, chemists can now analyze complex chemical datasets, identify patterns, and make predictions about chemical reactions, properties, and behavior. It enables researchers to make informed decisions and optimize experimental conditions.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Chemistry
Nowadays, only 4 out of 10 chemical companies widely implement AI in their operations.
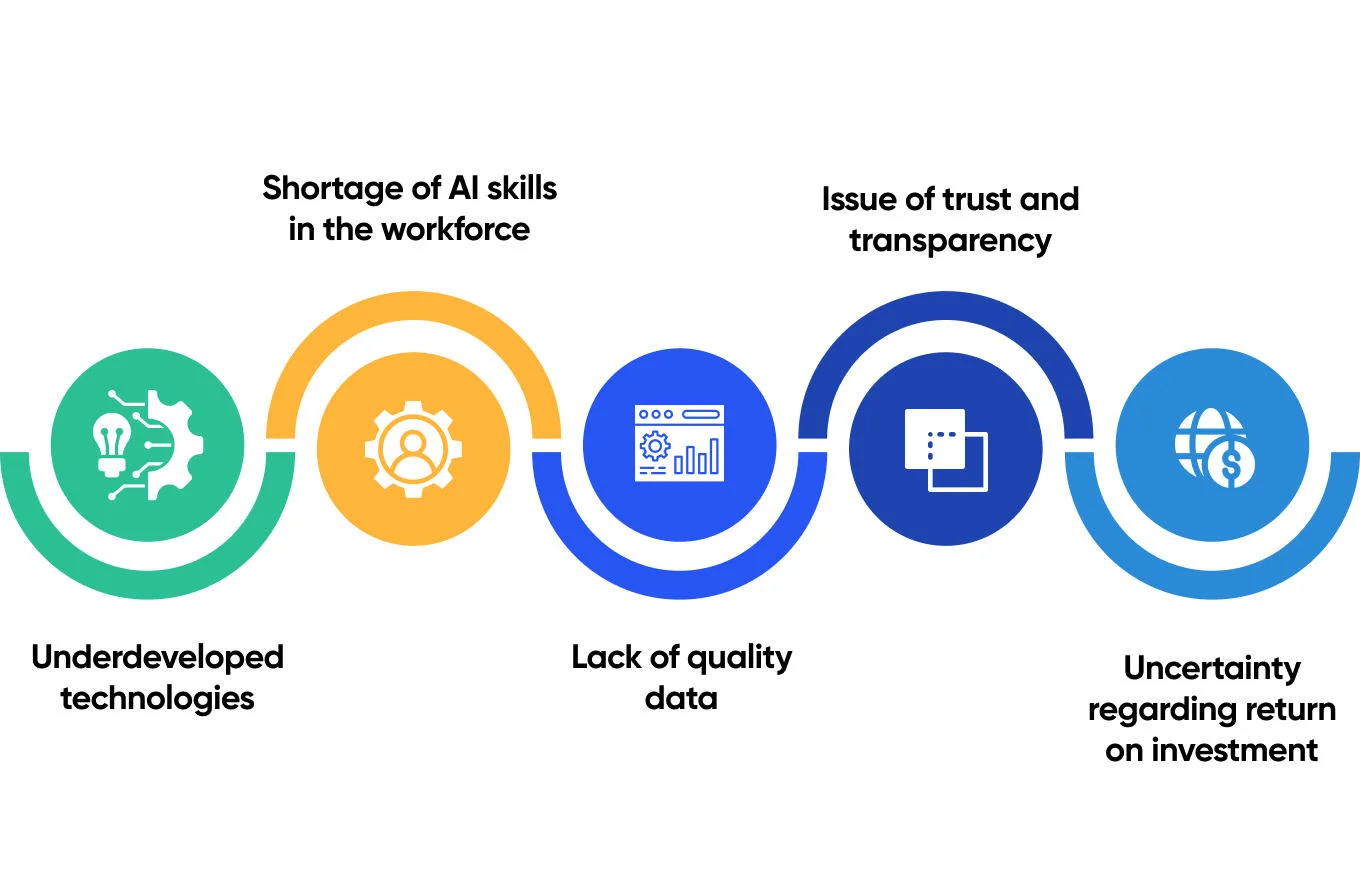
The reason why the process is so slow is caused by the challenges of AI implementation, including its costs, shortage of AI skills among employees, and more. Thus, before starting to use AI in your laboratory or CRO, it is vital to learn about its challenges:
- Underdeveloped technologies: Even though AI is widely used in areas like natural language processing or image recognition, it is only developing in the field of chemistry and R&D processes. Thus, its technologies are still underdeveloped, and it can be a challenge to tailor AI algorithms to meet complex laboratory requirements.
- Shortage of AI skills in the workforce: To use AI in chemical industry, you need experts in AI technologies. Unfortunately, it is highly challenging to find experts both in AI and domains required in CROs, chemical companies, and R&D departments.
- Lack of quality data: All AI algorithms rely on data to make predictions. In modern laboratories and CROs, data can often be incomplete or scattered across multiple sources. Moreover, there’s often a lack of standardization of data formats and protocols, making the process of AI usage even more challenging.
- Issue of trust and transparency: Chemical and pharmaceutical domains are highly regulated, requiring the highest levels of transparency and traceability. Thus, the lack of interpretability of AI models can affect the processes. It is essential to work on building trust between regulators, scientists, and stakeholders.
- Uncertainty regarding return on investment: Implementing AI technologies requires significant investments. You need to invest in infrastructure, software, and recruitment, but the return on investment (ROI) can be difficult to calculate. Moreover, it might be challenging to estimate the impact of AI on efficiency, cost savings, and scientific breakthroughs.
What Can AI Handle
Despite its challenges and limitations, AI can handle quite a lot in the chemical industry. It is possible to transform everything from drug discovery to material science and so on. Let’s talk about what AI can handle in detail.
Drug Discovery
Drug discovery might be one of the most critical application areas of AI in chemistry. Drug discovery has always been a long and daunting process that required a lot fo manual effort, money, and time. It can cost billions of dollars, and you can never be sure that everything will go right due to the possibility of human error.
With the development of AI technologies, scientists can now predict the properties of new drug candidates, identify potential targets for drug development, and optimize the design of drug molecules.
It is also possible to train AI and ML models to predict the activity and toxicity of new drug candidates. AI is also used to identify targets for drug development, such as proteins implicated in a specific disease.
Materials Science
AI technologies can be used to design new materials with specific properties, such as conductivity, strength, and flexibility. Researchers can also use AI and ML models to predict the properties of new materials and identify future candidates for studies.
It is also possible to use deep learning models to predict the properties of certain materials, such as predicting the melting point based on the crystal structure.
Chemical Synthesis
Another application of AI is the synthesis of chemicals, mainly creating new molecules or materials in the laboratory. Scientists can use AI to analyze the results of previous experiments and predict the outcomes of future ones. Moreover, AI assists in optimizing reaction conditions to reduce waste.
Disadvantages of Using AI in the Chemical Field
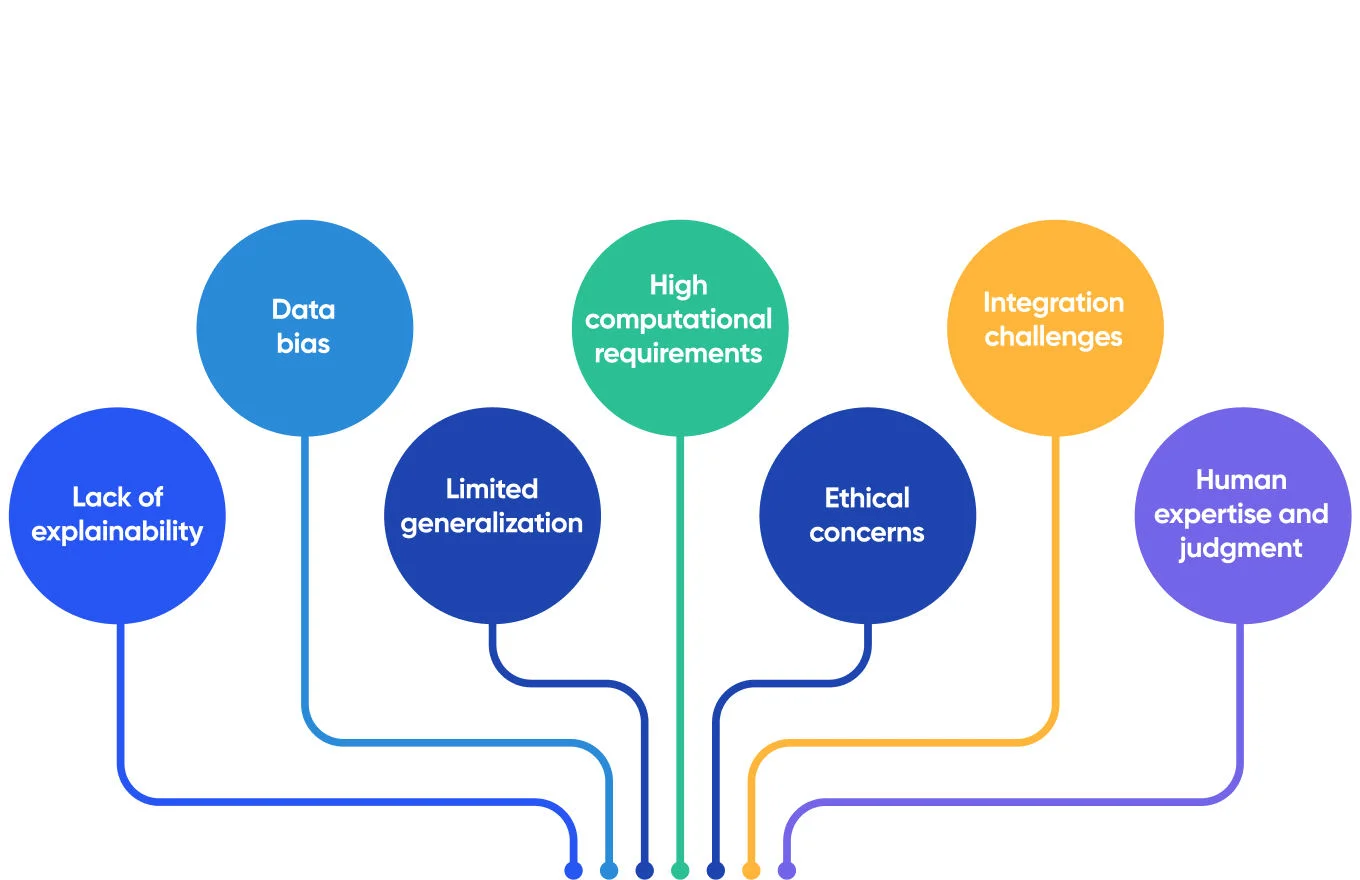
Despite the growing use of AI in the chemical field and its numerous applications, it’s still a relatively new concept that has a number of disadvantages and challenges that can affect the process if not researched enough and done right.
- Lack of explainability: AI algorithms often operate as “black boxes,” making it challenging to understand how they arrive at their predictions or recommendations. In the chemical industry, scientists and researchers must clearly understand the processes and reasoning behind AI-generated results so that it can cause significant issues.
- Data bias: AI models heavily rely on the quality and representativeness of the training data. If the training data contains biases or limitations, the AI model may perpetuate those biases, leading to biased predictions. It can lead to inaccurate assessments of chemical properties, environmental issues, and safety risks.
- Limited generalization: AI models are trained on specific datasets and may struggle to generalize well to new or unseen data. In the chemical field, modern compounds and reactions constantly occur, so it’s essential to be able to generalize beyond the training data.
- High computational requirements: Training and deploying AI models in the chemical field often require significant computational resources, including powerful hardware and extensive data storage.
- Ethical concerns: The use of AI in chemistry raises ethical concerns, such as data privacy, intellectual property rights, and the potential for misuse of AI-generated knowledge or compounds.
- Integration challenges: Integrating AI into existing laboratory workflows and infrastructure may require significant changes and adaptations.
- Human expertise and judgment: Human judgment and critical thinking are still essential in interpreting AI-generated results and making informed decisions in complex chemical research scenarios.
Future Prospects of AI in Chemistry
AI and ML technologies in the chemical industry are only at the beginning of their development, having a prosperous future in front of them.
With more and more chemical companies and CROs utilizing AI in their processes, these technologies will keep developing to meet these organizations’ growing demands and requirements. Let’s take a look at the future prospects of AI in chemistry.
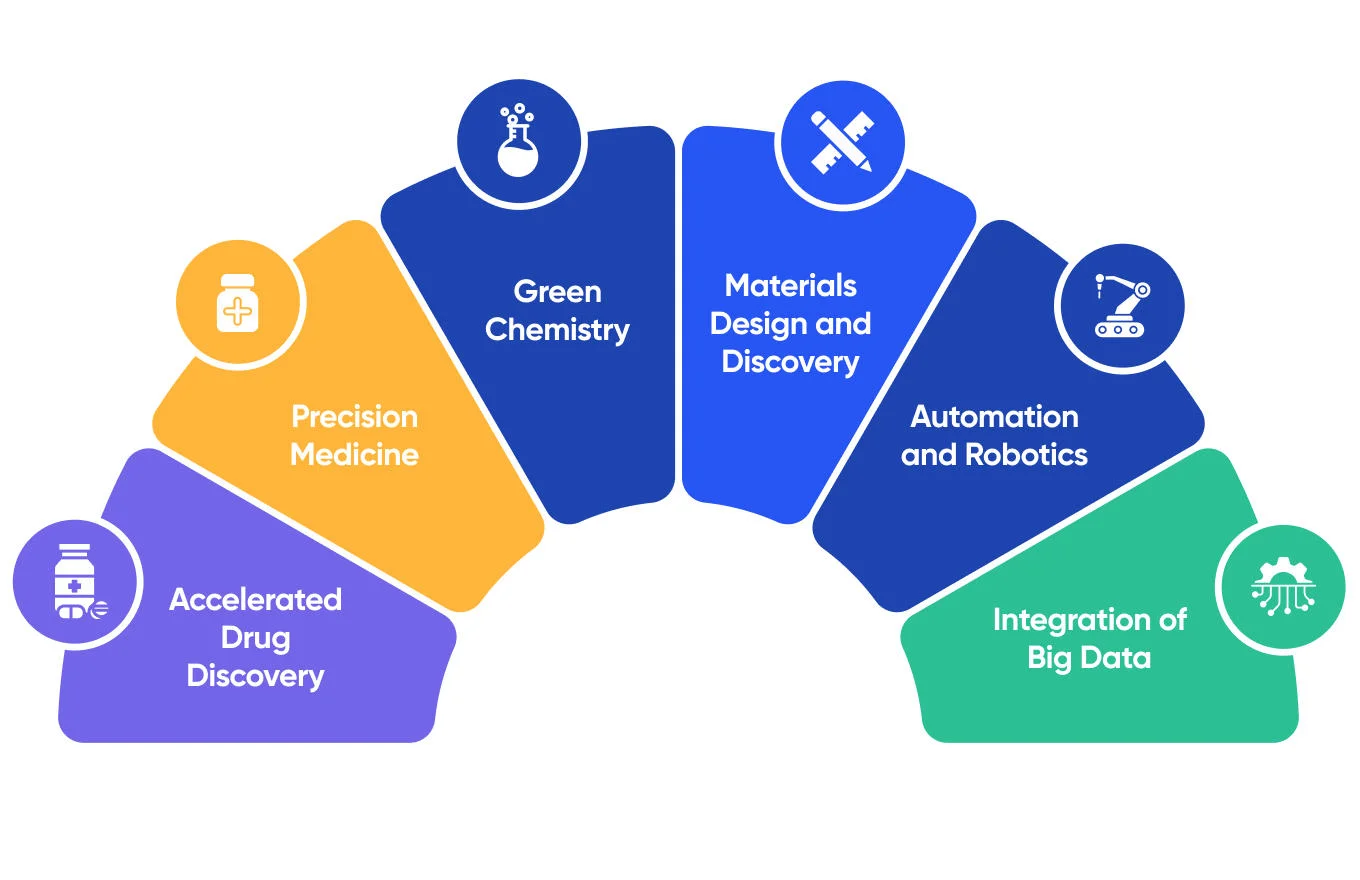
- Accelerated Drug Discovery: In the future, AI will revolutionize the process of drug discovery even further, by accelerating the identification of drug candidates.
By analyzing data from the past, AI technology will assist scientists in predicting the interactions of molecules and choosing the most suitable candidates for future testing. This can help scientists reduce time and money at the early stages of drug development as well as deeper explore the chemical space.
- Precision Medicine: Precision medicine’s main goal is to adjust medical treatments to patients based on their unique needs and characteristics. AI will analyze patient data, people’s medical records, and their lifestyles to identify patterns and precinct risks of certain diseases and treatment outcomes.
- Green Chemistry: There’s a trend towards more sustainable and green chemical practices right now, and AI can help achieve this faster.
AI can analyze chemical reactions and environmental impacts and design more efficient, environmentally friendly compounds. With the use of AI, it will be possible to minimize waste generation and promote more sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Materials Design and Discovery: AI can help scientists design and discover new materials with desired properties. With the use of AI and ML, chemists will be able to predict new materials with characteristics like conductivity, strength, and catalytic activity.
- Automation and Robotics: Combining AI with robotics can help automate laboratory processes and enhance productivity. Robotic systems that utilize AI can perform routine, repetitive tasks such as data analysis and sample preparation faster and more effectively. This helps researchers focus on more important tasks and reduce the risk of human error.
- Integration of Big Data: The chemical industry is all about data. It generates information from simulations, experiments, studies, research, and other sources. It is essential to collect, store, and analyze this data properly, and AI can assist with that. In the future, AI will be able to analyze this data to uncover trends and hidden relationships and generate new hypotheses.
Conclusion
Utilizing AI in the chemical industry, especially in laboratories and CROs, is one of the main ways to revolutionize and streamline processes. It helps these organizations analyze data, make predictions, and come up with new solutions that have not been available without AI.
Even though the application of artificial intelligence is still to reach its full potential in chemistry, it is highly likely that it will transform the industry in the coming years. Thus, it’s time to join this trend and use AI to your best benefit. If you need a consultation, contact us.
FAQ
AI has several benefits for chemical companies: it helps optimize processes, controls the quality of products and components, assists with predictive maintenance, and accelerates the research and development process in the industry.
AI is applied in various areas of chemistry, helping enhance research, development, and operational processes. Usually, AI is used in drug discovery, materials design, reaction optimization, spectroscopy and analysis, process control and optimization, and computational chemistry.
Thanks to the application of AI, chemistry has made some notable achievements in drug discovery, mainly the ability to identify potential drug candidates and predict the efficiency, safety, and pharmacokinetic properties of drug candidates. Moreover, it is now possible to discover new materials with tailored properties. Finally, AI helps optimize chemical manufacturing processes by analyzing real-time data and guiding process control.