Medical Software Development: Industry Guide

Medical Software Development Definition
Medical, or healthcare software, is a vital part of the modern healthcare industry. Software development for the medical industry is the process of creating and designing software applications and solutions tailored to specific use cases in the healthcare industry.
It is the development and implementation of software solutions built for healthcare professionals, patients, laboratories, and other healthcare organizations to help them streamline workflows, facilitate accurate data management, and enhance patient care.
Custom medical software for industries includes patient engagement tools, admin dashboards, telehealth, and telemedicine apps, data analysis tools, remote patient monitoring, and electronic health records (EHR) systems, mobile health (mHealth) apps, and more.
Now, let’s talk in detail about the types of medical software that are now used by health organizations.
Types of Medical Software
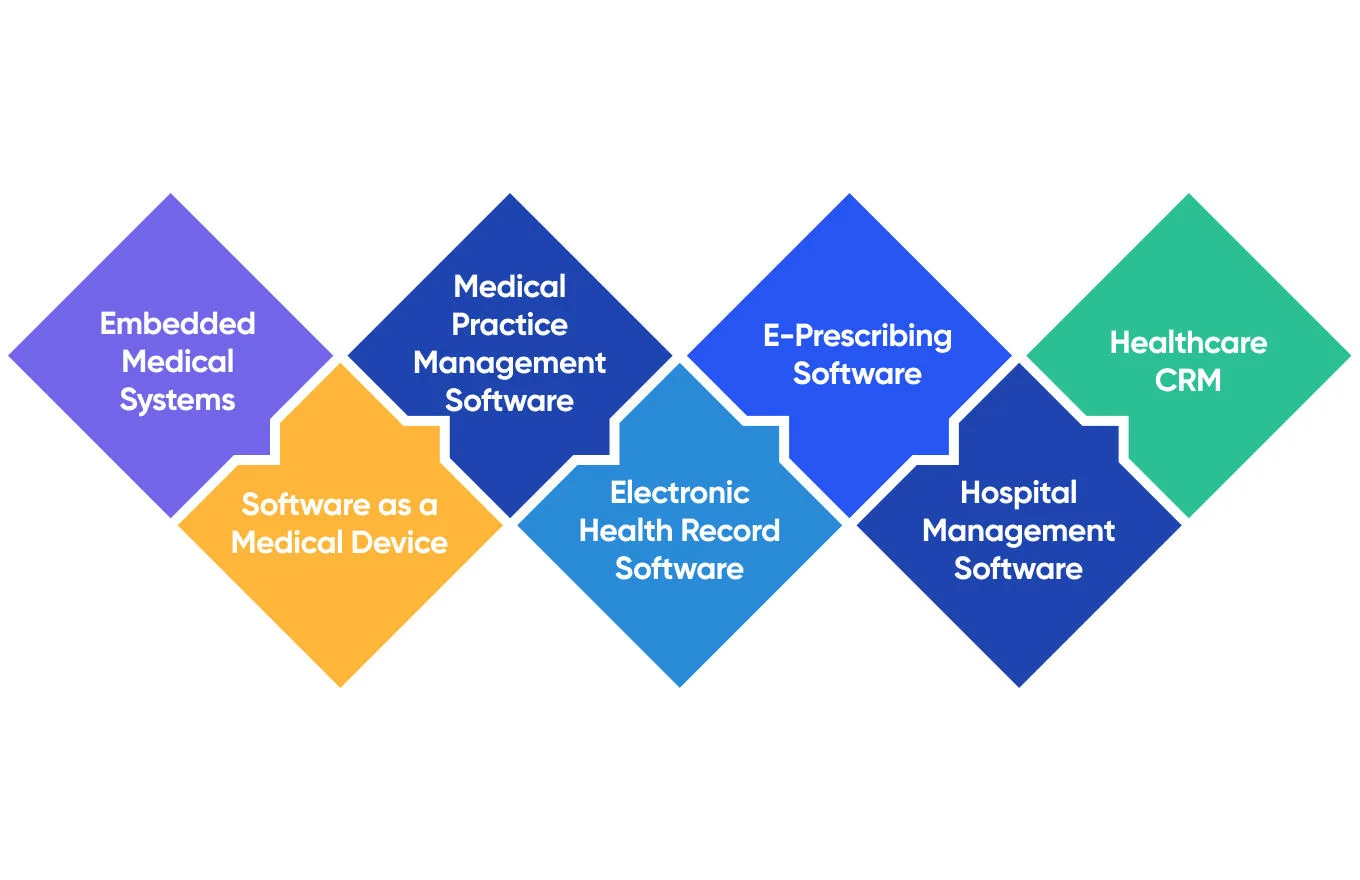
- Embedded Medical Systems and Embedded Medical Software Development: Embedded systems in healthcare have been there for a while. They refer to the integration of medical devices or systems with embedded technology, such as sensors, microprocessors, and software.
These tools are used for making diagnoses, monitoring, and supporting functionalities in healthcare settings. This type of software runs on medical devices or equipment, acquiring and processing data and presenting it to healthcare professionals or patients.
- Software as a Medical Device (SaMD): The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) defines SaMD as software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes that perform these purposes without being part of a hardware medical device.
For example, these solutions run on laptops, desktops, mobile devices, and more. They are used for patient imaging, scan analysis, sound monitoring, and remote ECG monitoring.
- Medical Practice Management Software: PM software helps medical offices run more efficiently by managing daily operations like financial and administrative functions or connecting them to medical records.
The capabilities of PM software include tracking patients, scheduling appointments, performing billing procedures, submitting insurance claims, and more.
- Electronic Health Record Software: This type of software can be thought of as a digital version of traditional paper patient charts. It uses standardized formats to share patient data efficiently between different healthcare providers. It is a repository of patient data such as medical history, treatment plans, diagnoses, medications, allergies, and more.
- E-Prescribing Software: This software helps healthcare practitioners enter prescription information into a device and transmit this data to pharmacies using the program designed to connect to a transmission network.
- Hospital Management Software: Hospital management software or system (HMS) is a solution that helps manage the data related to health care and aids in the job completion of health care providers efficiently. It assists in billing, managing patient information, assigning insurance, and administrative work.
- Healthcare CRM: It is a special solution designed for a medical organization such as a hospital, a medical center, a laboratory, a clinic, etc. It helps automate customer management processes, keep clients’ data up to date, and regulate administrative tasks to focus on the needs of patients.
Advantages of Medical Apps
Medical apps are the future of the healthcare industry, helping organizations automate their processes, improve patient engagement, minimize the risks of misdiagnosis, and more. Let’s take a look at the main benefits of medical software for specialists, patients, and health organizations.
Benefits for Clinical Specialists
- Streamlines workflows: Medical applications help specialists automate routine tasks such as documentation, prescriptions, appointment scheduling, and more. By automating these tasks, specialists can set priorities easier and focus more on patient care.
- Access to critical information: Medical applications also provide easier access to vital patient data, their records, and drug databases. Some types of medical software include decision support tools that help specialists make more data-driven decisions and improve diagnosis. Moreover, having all this data in one place helps prescribe more accurate treatment plans to patients.
- Enhanced communication: Medical software helps healthcare practitioners communicate more efficiently, share patient data, collaborate, and consult easier.
Benefits for Patients
- Improves access to care: With the help of medical software, patients can access healthcare services from their devices remotely, which eliminates the need for in-person visits. Moreover, it is possible to receive prescriptions or consultations online.
- Empowerment and engagement: Patients can use medical apps for medication reminders, health tracking, self-monitoring, and more. Some apps also include educational resources that can help patients learn and participate in their healthcare. What is more, medical apps help patients make more informed decisions.
- Convenience and time-saving: The use of medical apps helps patients schedule appointments faster, have their medical records in one place, and be able to access them, receive their test results, and contact their doctors when needed.
Must-Have Features of Medical Software Development
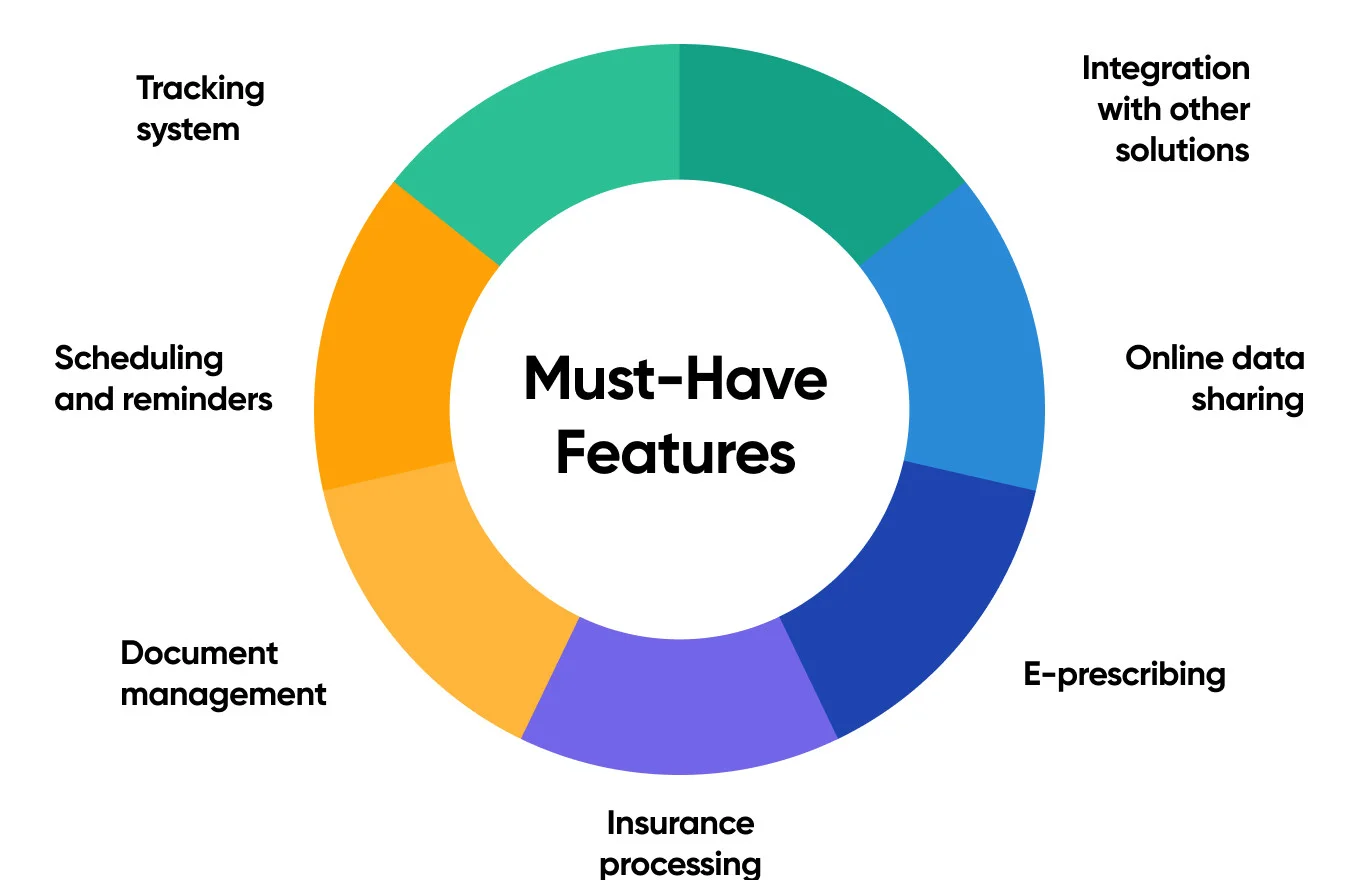
Even though there are different types of medical software and their set of features can vary depending on the healthcare needs, there is a set of features that are a must-have for all medical apps.
- Tracking system: Any medical app should allow healthcare practitioners to monitor patients’ vitals and conditions. The primary function of this software should be to monitor heart rate, blood pressure, pulse, blood sugar level, etc. All this information should be collected and stored in the system for future use, current diagnosis, and treatment.
- Scheduling and reminders: If it is an ERM system, it should have the scheduling and reminders feature. Physicians or nurses should be able to schedule appointments and follow-ups and send reminders to patients about them.
- Document management: Medical software’s other essential feature is the ability to manage documentation. It includes retrieval and management of patient information from lab results, prescriptions, and so on.
- Insurance processing: Medical software must provide the ability to process insurance claims as required by a healthcare provider’s contract.
- E-prescribing: Some modern medical software solutions have a new feature that allows practitioners to send prescriptions online to their patients without the need for in-person visits. Moreover, patients can choose the pharmacy they want to go to, and healthcare providers will take that into account.
- Online data sharing: If you use enterprise healthcare solutions, it must have a feature that allows sharing data among different institutions: clinics, hospitals, laboratories, etc. This helps manage and process data faster and supports the interoperability protocol between hospitals, clinics, and software vendors.
- Integration with other solutions: Integration of medical software with other solutions is vital for ensuring seamless and efficient healthcare operations. This software can be integrated with EHR systems, medical imaging systems like Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Radiology Information Systems (RIS), Laboratory Information Systems (LIS), pharmacy systems, Health Information Exchange (HIE), and more.
The Life Cycle of Medical Software Development
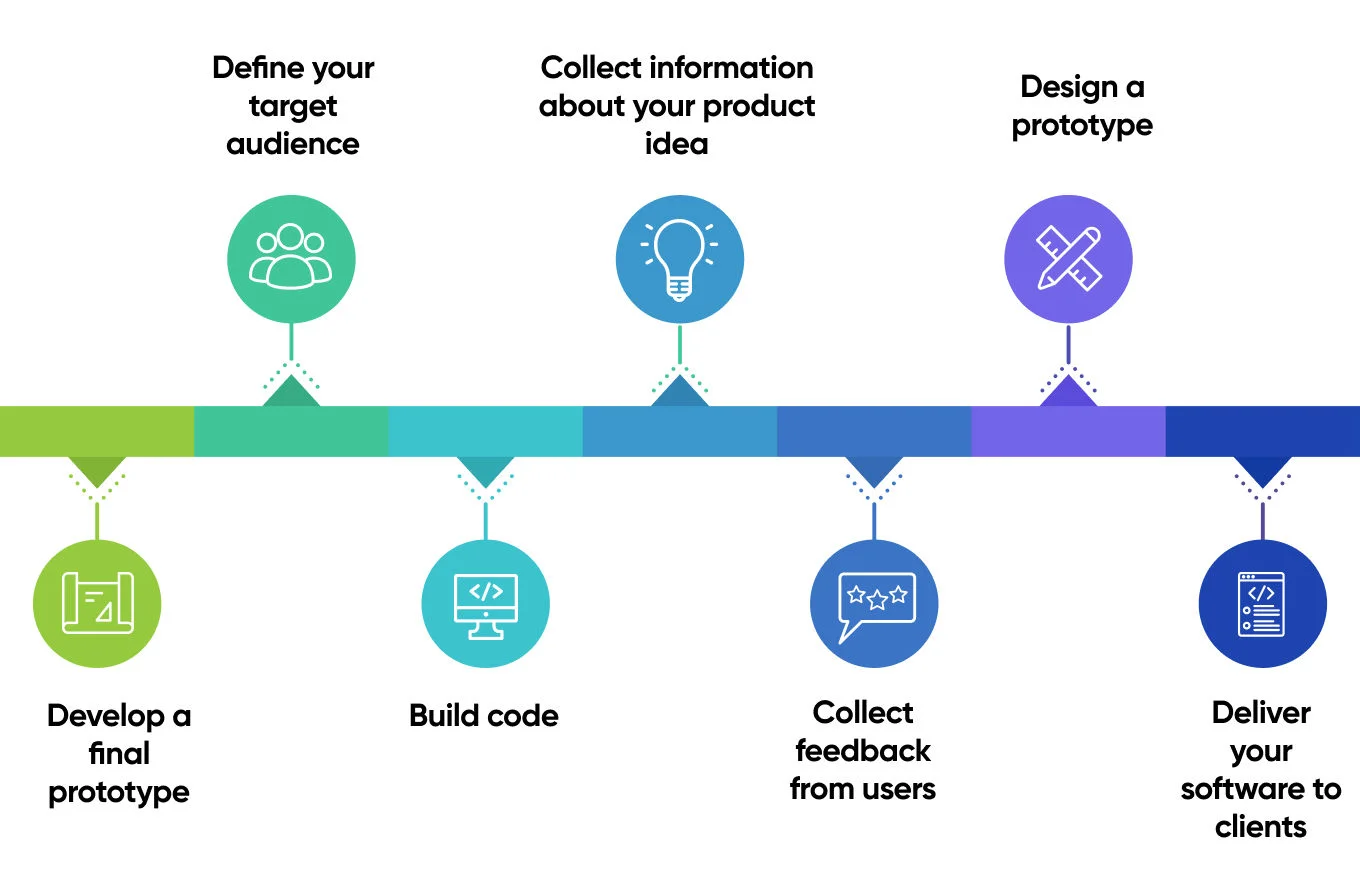
The steps of medical software development depend on your organization’s needs and requirements, budget, and whether you have an in-house team with enough expertise to develop this solution. In general, there are 7 steps to this process:
- Define your target audience: First of all, you need to clearly understand who you are developing the solution for. It is essential to be aware of your target audience’s needs and preferences. If you outline them well, both the client and the user will benefit from having a clear vision of the future application.
- Collect information about your product idea: Once your target audience is defined, you need to gather essential information about the product idea. To do that, you need to conduct thorough research to understand industry trends, challenges, and potential opportunities. You can perform competitor research for that, and gather insights from end-users, stakeholders, and healthcare providers.
- Design a prototype: After the information is collected, the development team starts working on the prototype. Simply put, it is a working model of your software with basic functionality that demonstrates to the stakeholders the concept before proceeding to full-scale development.
- Develop a final prototype: The initial prototype needs to be validated before the development team can start working on the final prototype. It has more features, a user interface, and other adjustments based on the gathered feedback and additional requirements. The final prototype looks almost like the final product.
- Build code: After the final prototype is agreed upon, it’s time to write code to develop the solution. This step involves the choice of programming languages, frameworks, and libraries.
- Collect feedback from users: During the development process, it is essential to gather feedback as the process goes on. Asking for feedback from the users will help you improve the features and functionalities and fix functional gaps, bugs, and performance concerns. You can collect feedback through surveys, user testing sessions, or pilot implementations.
- Deliver your software to clients: Finally, once the software solution is finalized, it is ready to be deployed. During this step, medical software is tested for quality assurance and regulatory compliance and delivered to the clients. Usually, development companies also provide support and maintenance after deployment to ensure that everything is working flawlessly.
How Can SoftFormance Help You in a Software Development Project in Healthcare
At SoftFormance, we have more than 10 years of experience in software development in various industries, such as education, fintech, travel, chemical, solar, medical, and healthcare.
We specialize in healthcare application development for medical services, helping them automate routine processes, boost patient care, organize medical documentation, and medical management.
Here is the list of medical software services we provide:
- Lab management software development
- Healthcare app modernization
- Medication marketplace development
- Medical management software development
- Healthcare accounting software development
- Medical software integration
- Developing apps for condition treatment
- Healthcare automation
We ensure that all solutions we develop for our clients are HIPAA compliant, are available on mobile devices, and are easy to integrate with other solutions and technologies. Moreover, when developing custom solutions for the medical industry, we involve IoT, AI and Machine Learning, and Cloud technologies.
If you have been interested in developing medical software solutions for your organization and looking for a development partner, contact us.
Conclusion
In conclusion, medical software has revolutionized the way healthcare facilities handle patient engagement, collect, analyze, and store data, and work on treatment plans and consultations.
A custom medical solution that is built according to the specific needs of an organization and its patients can help streamline and automate processes and address critical challenges and deliver tangible benefits.
Nowadays, utilizing the benefits of medical software development is not a trend; it is a necessity if you want to stay on top of the ever-evolving landscape of modern healthcare. For a consultation, feel free to contact us.
FAQ
You should consider the domain expertise of the team, years of experience, successful cases, and technical skills. Moreover, check their understanding of security and privacy practices, compliance knowledge, and their collaboration and communication skills.
The budget for medical development depends on factors like project requirements, development complexity, the team working on the project, timeline, resource allocation, and market rates.
According to the recent statistics, the medical software market size is about to touch $104.1 billion by 2020.
In healthcare, the top types of software used include EHR systems, practice management systems, medical imaging software, HIE systems, Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS), BI, and LIMS systems.
Thank you for sharing the “Medical Software Development: Industry Guide.” It’s great to have comprehensive resources like this to navigate the complexities of the medical software development industry.
Are you guiding the medical software development information it will be very helpful for developing the particular software regarding the medical apps. Sharing advantages of the medical software and which feature are required in the software. Thanks for sharing this informative article with us keep sharing