Benefits of Laboratory Process Mapping

- Do You Really Know What Is Happening in Your Laboratory?
- Why is Process Mapping so Important for laboratories?
- Process Mapping Benefits for LIMS and ELB Implementation Projects
- How to Do Process Mapping in Your Laboratory?
- 7 Steps to Create Your Process Map
- Standards and Tools for Process Mapping
- Summary
- FAQ
While lab digitization is a very popular trend among businesses and organizations that rely on laboratories, it all starts with understanding the processes.
Regardless of the digital solution you’re implementing, you should know what processes are handled in your laboratory and how.
So, long before you start to digitize and improve your laboratory management, you should focus on process mapping, which is the first and the vital step in laboratory digitization.
What is process mapping? How does it help laboratories succeed? What are the essential steps and points to consider while mapping your lab processes?
Keep on reading to get answers to these questions and map out your lab processes the right way.
Do You Really Know What Is Happening in Your Laboratory?
Let’s start with a process mapping definition and clarify what is a process map.
In brief, laboratory process mapping involves visual documentation of the current as-is state of a process in a laboratory.
The problem is that lab processes described in the documentation and the actual processes handled in the laboratory are often very different.
For example, a custom synthesis company can be officially oriented on developing custom specialty chemicals. However, in reality, this lab focuses on quality assurance for the existing fine chemicals.
So, the main purpose of process mapping is to help organizations visualize and understand their lab processes with attention to real responsibilities, timelines, and dependencies.
Only a complete understanding of your processes will help you improve your lab performance and successfully digitize your laboratory, regardless of the industry.
Why is Process Mapping so Important for laboratories?
But these were rather general facts on lab process mapping. Why is this activity so important?
Whether you’re running an R&D laboratory, a Contract Research Organization, or a Custom Synthesis lab, you should never underestimate lab process mapping.
Otherwise, you will most likely:
- Lack the understanding of your processes;
- Not understand your weaknesses and opportunities for improvement;
- Be unprepared for chemical industry challenges and and issues peculiar to any other domain;
- Lack the understanding of your process dependencies and connections;
- Lack the understanding of corresponding rules and regulations, such as MDSDS, FDA, MSDS, ISO9001, cGMP, OSHA, and the ways to comply with them.
Process Mapping Benefits for LIMS and ELB Implementation Projects
And the next logical point you should consider is the diversity of actual lab process mapping benefits. With these advantages, you can easily take your lab efficiency to the next level.
Control over the Inventory
While managing a lab, especially when it comes to custom synthesis companies, you should track a great range of components and inventory parts.
To handle everything the right way, you should understand your active ingredients and potency management practices, as well as track your warehouse conditions.
Lab process mapping helps you cover this challenge, as well as understand the ways to manage your bulk storage and warehouse for ingredients and finished goods more efficiently.
As a result, you will minimize or even get rid of the most significant inventory-related problems in your laboratory.
Understanding of Collaboration Patterns
To develop the right digitization solution and to manage your lab staff more efficiently, you should precisely understand your collaboration patterns.
This means outlining the responsibilities, interactions, communication channels, and task assignment platforms relevant to your laboratory staff.
And it’s always better to visualize these connections and responsibilities as a part of comprehensive lab process mapping.
Clear Quality Control Process
Quality control is one of the most common and responsible lab processes, no matter the industry.
For example, if your CRO (Contract Research Organization) fails to run it properly, your product can harm its end-users, which will make you liable.
A typical approach to lab QA involves four consecutive stages: raw material testing, synthesis testing, chemical reaction product testing, and pre-sales testing.
Checking out whether your QA practices correspond to this pattern is, for some organizations, the very purpose of a process map.
And if your QA approach is organized differently, make sure to display it on your process map and check its compliance with the corresponding regulations.
Understanding Data Collection Points
If you are working in the healthcare industry, you should be extremely attentive to your data practices. Otherwise, you can be fined under the HIPAA rules.
And many other industries that rely on lab testing have similar regulations.
That’s why efficient data management is mandatory for your laboratory.
One of the biggest process mapping benefits is that it allows you to detect data collection points. As a result, you will ensure that data from all these points are stored in corresponding storage and conditions.
First, it will secure you from a messed up approach to data, where all information on reactions, compounds, active ingredients, and other important things are stored in one place or stored inconsistently.
Secondly, you will label sensitive data, store it with more attention to security, and avoid any security violations.
Understanding of Your Challenges
Lab process mapping helps you understand your lab challenges that may be challenging to identify without in-depth insight into your processes.
For example, there may be a minor inconsistency in units of measurement considered during your lab trials.
As a result, your lab team should spend time synchronizing the result of your trials.
Meanwhile, lab process mapping will help you detect this problem at the very start. As a result, you may standardize specific units of measurement and get more consistent reports of lab trials without the need to synchronize them retroactively.
Regulation Compliance and Improved Auditing
Auditing and reporting are essential for different laboratories.
And you can efficiently automate these processes with lab digitization solutions.
But first, you should understand your processes and auditing needs through process mapping.
One of the greatest benefits of process mapping is that it will show how your lab activities interact with MSDS, ISO9001, CGMP, OSHA & GHS rules and regulations.
What’s the outcome?
You keep the information on all the relevant regulations in one place and easily track your process compliance with these rules.
Dynamic Visualization of the Process
Laboratory process mapping done the right way allows you to create an interactive map of your processes. This map can be later integrated with your lab digitization solution.
This brings you a detailed visualization of your lab processes.
And this visualization means more control and visibility of your lab activities, infrastructure, and dependencies.
Also, a good visualization allows even your specialists with no technical knowledge to improve their understanding of your laboratory activities and practices.
How to Do Process Mapping in Your Laboratory?
From our experience of dealing with chemical industry companies and labs from other domains, there are universal suggestions on how chemical industry processes should be organized.
Here’s a shortlist of the most important points to consider:
- Engage the right people;
- Note everything;
- Create as many schematics images and other visuals as possible;
- Use the SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, Customers) diagram whenever possible;
- Confirm your process maps with people having an in-depth understanding of your processes.
7 Steps to Create Your Process Map
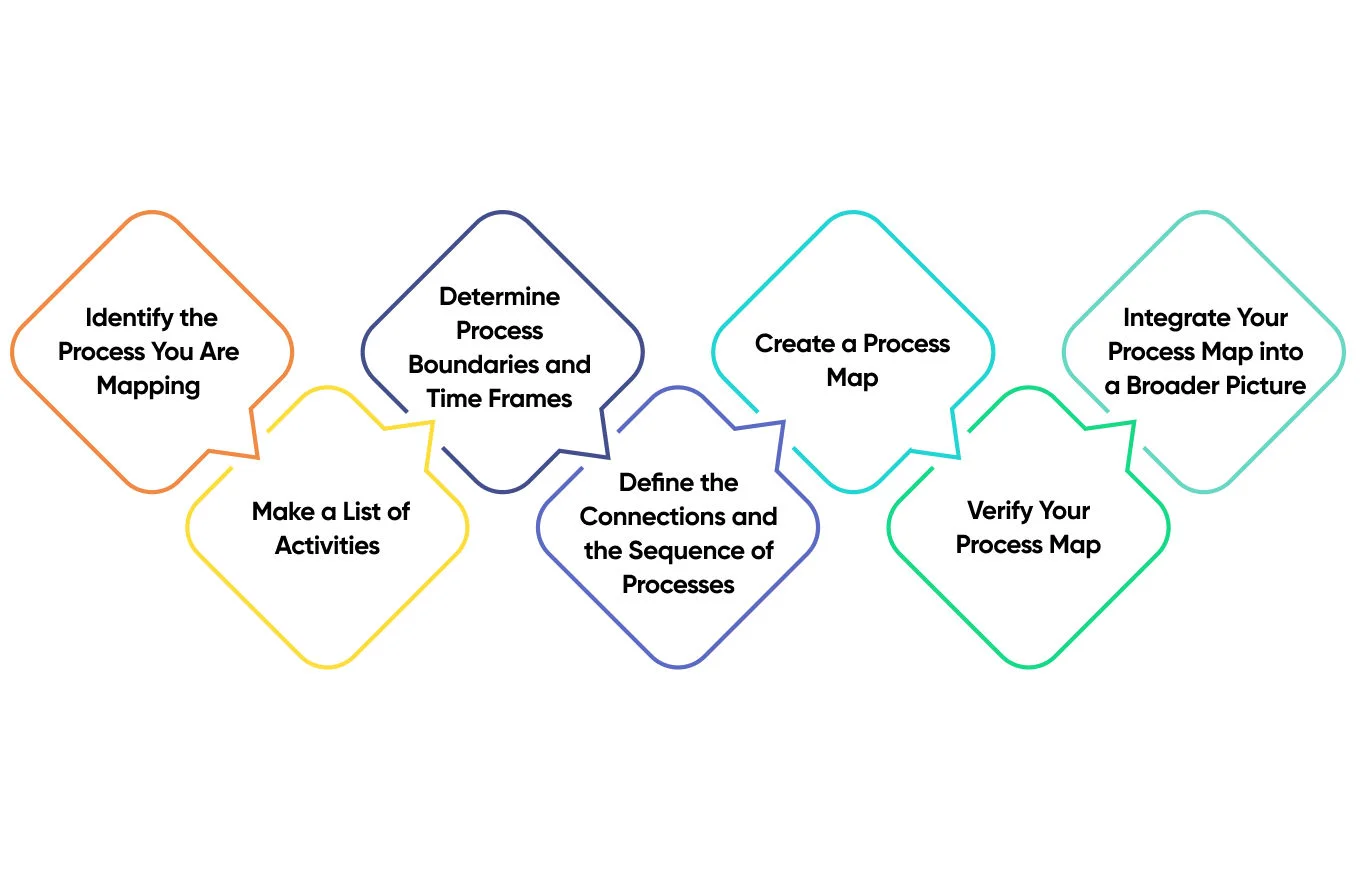
Now, let’s proceed with a 7-step methodology that will help you come up with the most deliberate and efficient process map. Experience shows that it is a universal approach that, roughly, fits most laboratories serving most industries.
1. Identify the Process You Are Mapping
First, define the process or processes you are mapping. It means that you should have a clear understanding of lab processes and the differences between them.
For example, you should determine whether you’re mapping out inventory management activities, custom synthesis tasks, formula adjustments, reporting, or quality assurance processes.
The next step is finding a person responsible for your chosen process. Ask questions to get an in-depth understanding of the process and process mapping meaning.
2. Make a List of Activities
Asking questions is mandatory because it will allow you to drill through the process and come up with a detailed list of activities.
Just make sure that you write down all of these activities.
Later, you will be able to run through the list and leave only the most relevant activities on your process map.
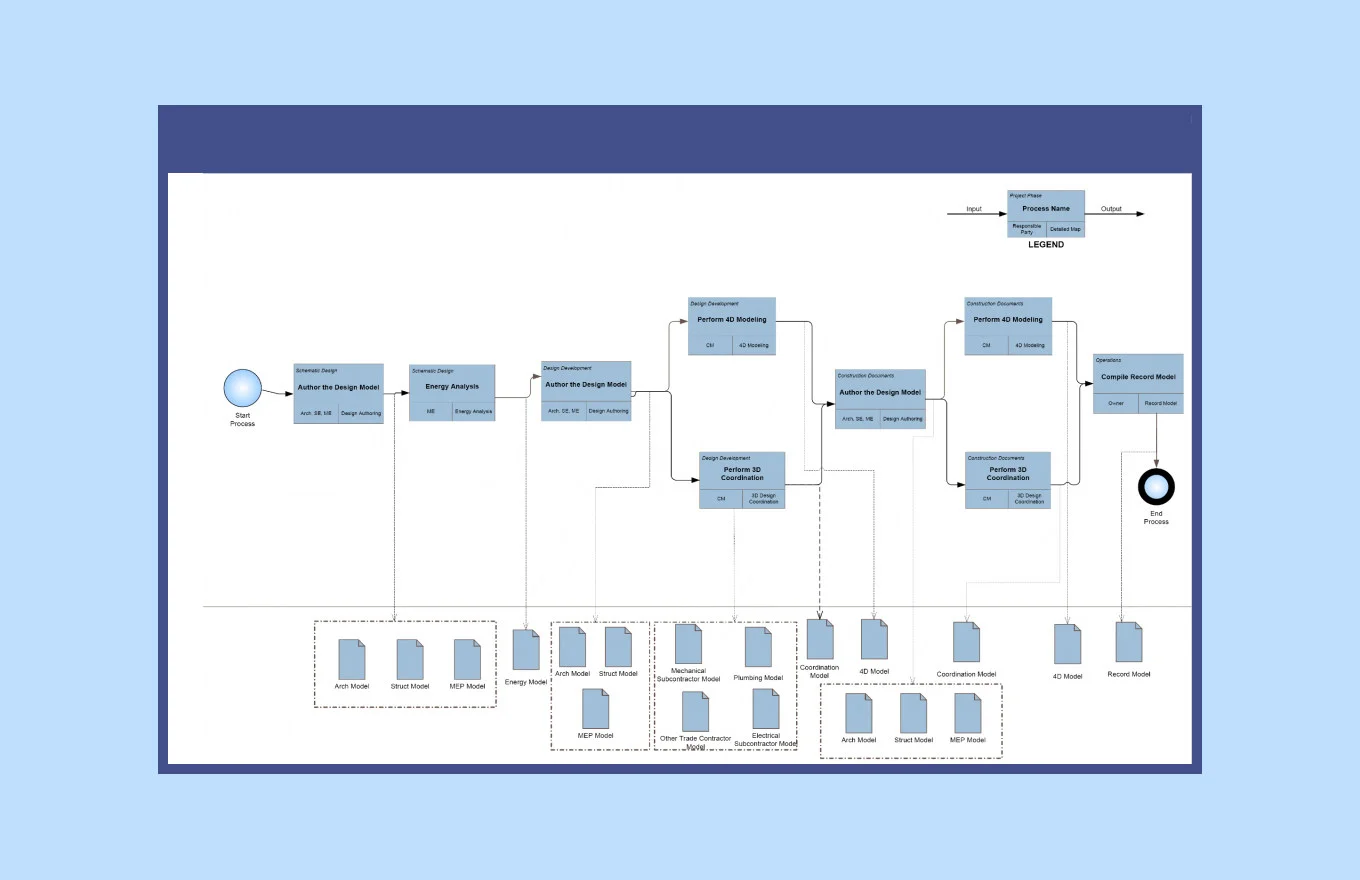
3. Determine Process Boundaries and Time Frames
Make sure to determine time frames and boundaries for all the activities.
It will help you plan the schedule more efficiently.
This scheduling can be later implemented in your lab digitization software.
4. Define the Connections and the Sequence of Processes
Lab processes don’t exist as standalone activities.
For example, batch preparation is always followed by batch process synthesis, so these two activities are densely interconnected.
To create a comprehensive and broad process map, you should clearly define the connections between your processes, as well as their sequence.
You can later use this knowledge for implementing a broad map for all your lab processes.
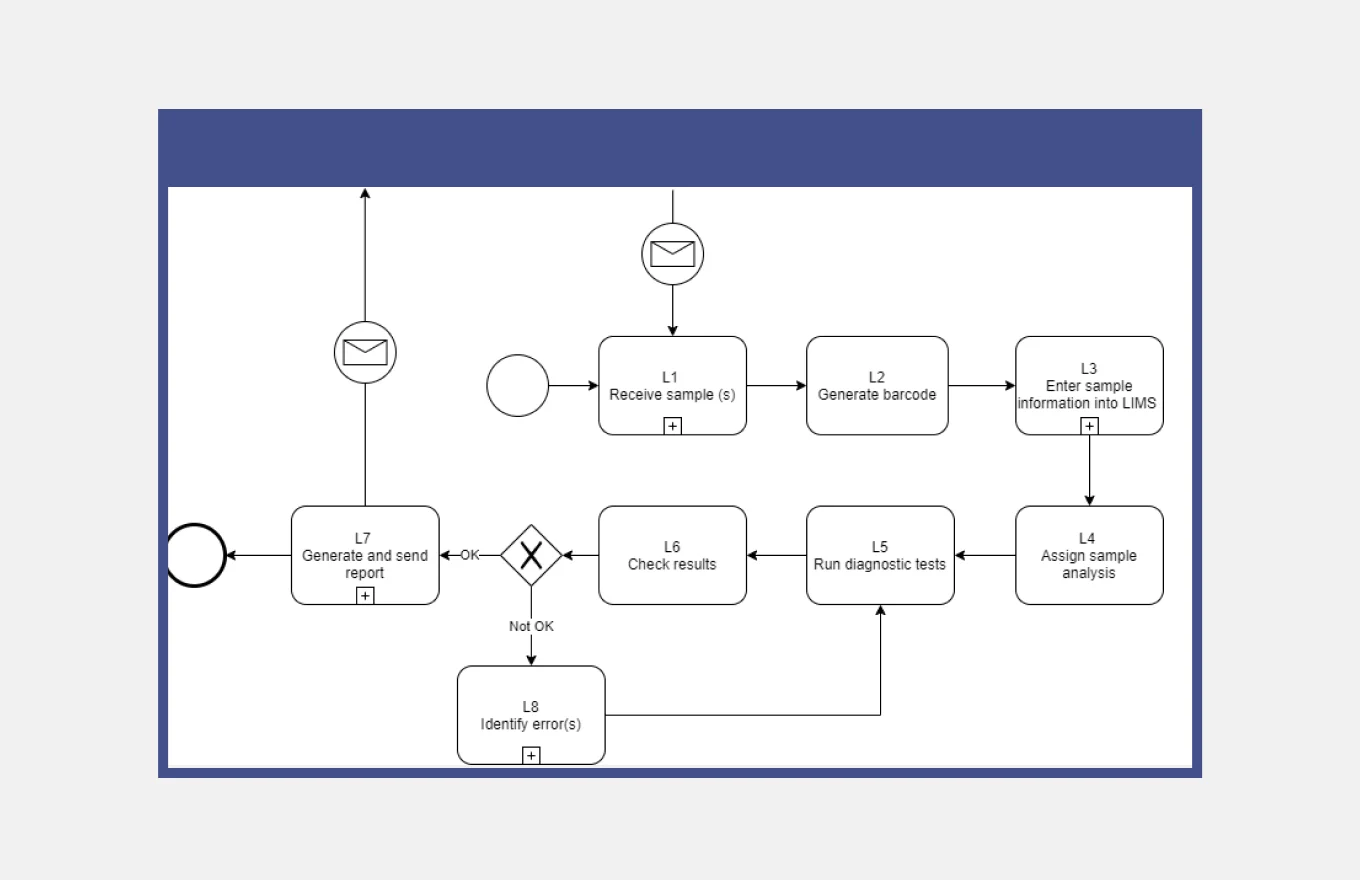
5. Create a Process Map
Once you have all the required information, start building a process map.
A popular option is creating a SIPOC map, which clearly outlines suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers related to your process.
You can also go with a value stream map (VSM). In this case, you will create a process map with very deliberate attention to detail. A VSM is user-centric by design and displays not only the flow of work but also the flow of information and materials in the process.
For example, a VSM for quality assurance in a CRO laboratory should identify possible risks that the violation of QA principles can bring to an end-user.
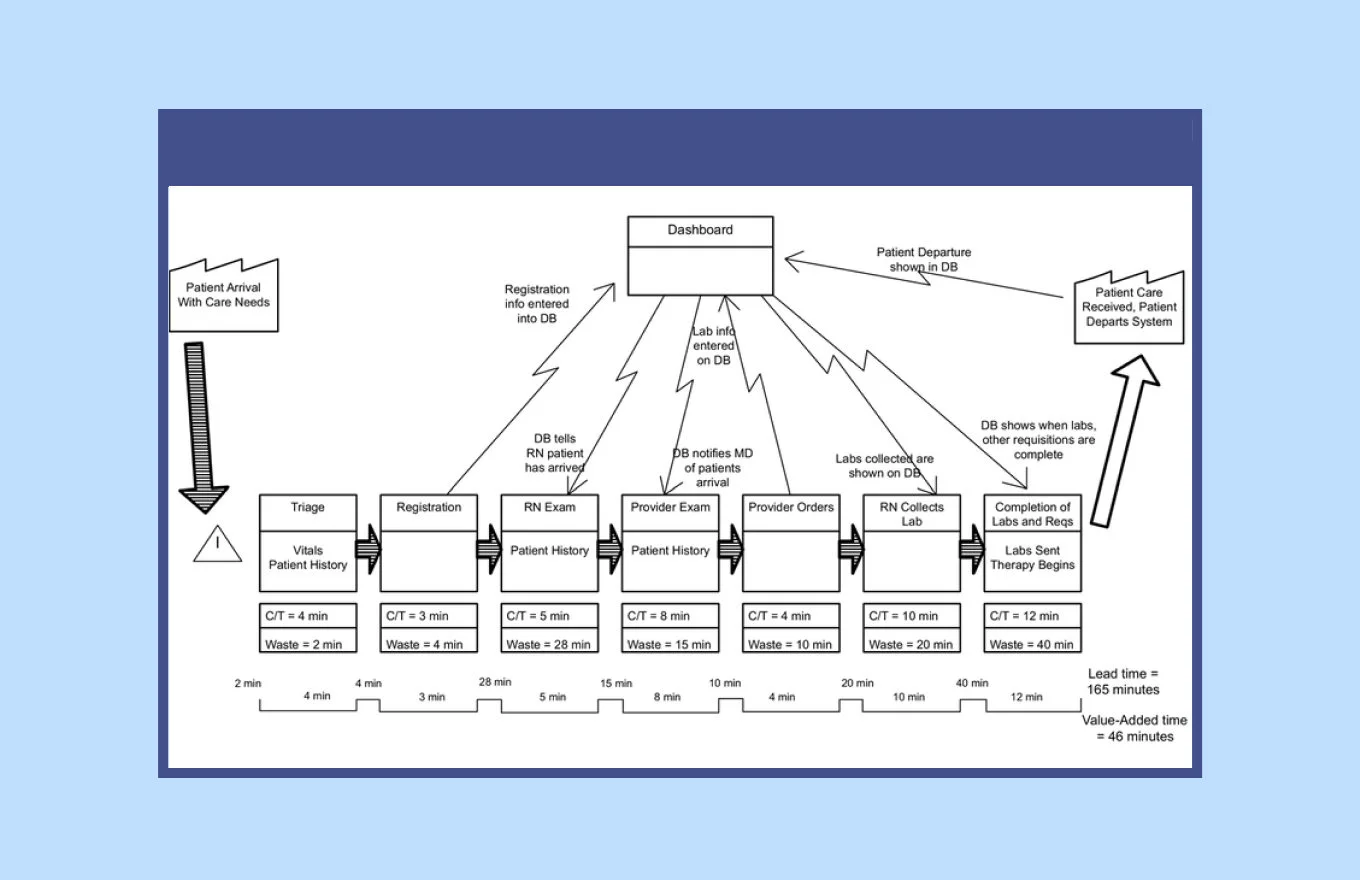
You can also choose any other process map design you want. The key point is to make the map understandable and make sure that no important information is missed.
6. Verify Your Process Map
Once your process map is completed, it is important to validate it with stakeholders involved in the process.
Their feedback will assure you that the chart is accurate and, if needed, help you address the gaps.
Additionally, a thorough expert review will help you ensure that no important information is missed.
7. Integrate Your Process Map into a Broader Picture
Once the process map is completed, keep on improving it.
Also, as I’ve already mentioned, make sure to display its connections with other processes. This will help you come up with a broader picture of your laboratory processes.
Ideally, you will come up with a grand and highly-detailed scheme for all your lab processes.
It can be later easily integrated with your lab management solutions.
Standards and Tools for Process Mapping
Here are just a few additional tips that will help you understand how to do process mapping properly.
To have a more consistent process map, follow the widely accepted mapping standards.
The first one is the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard.
It is a standard widely used for designing graphical representations of business processes.
BPMN is based on a flowchart design and has four main elements to it:
- Flow objects
- Connecting objects
- Swim lanes
- Artifacts
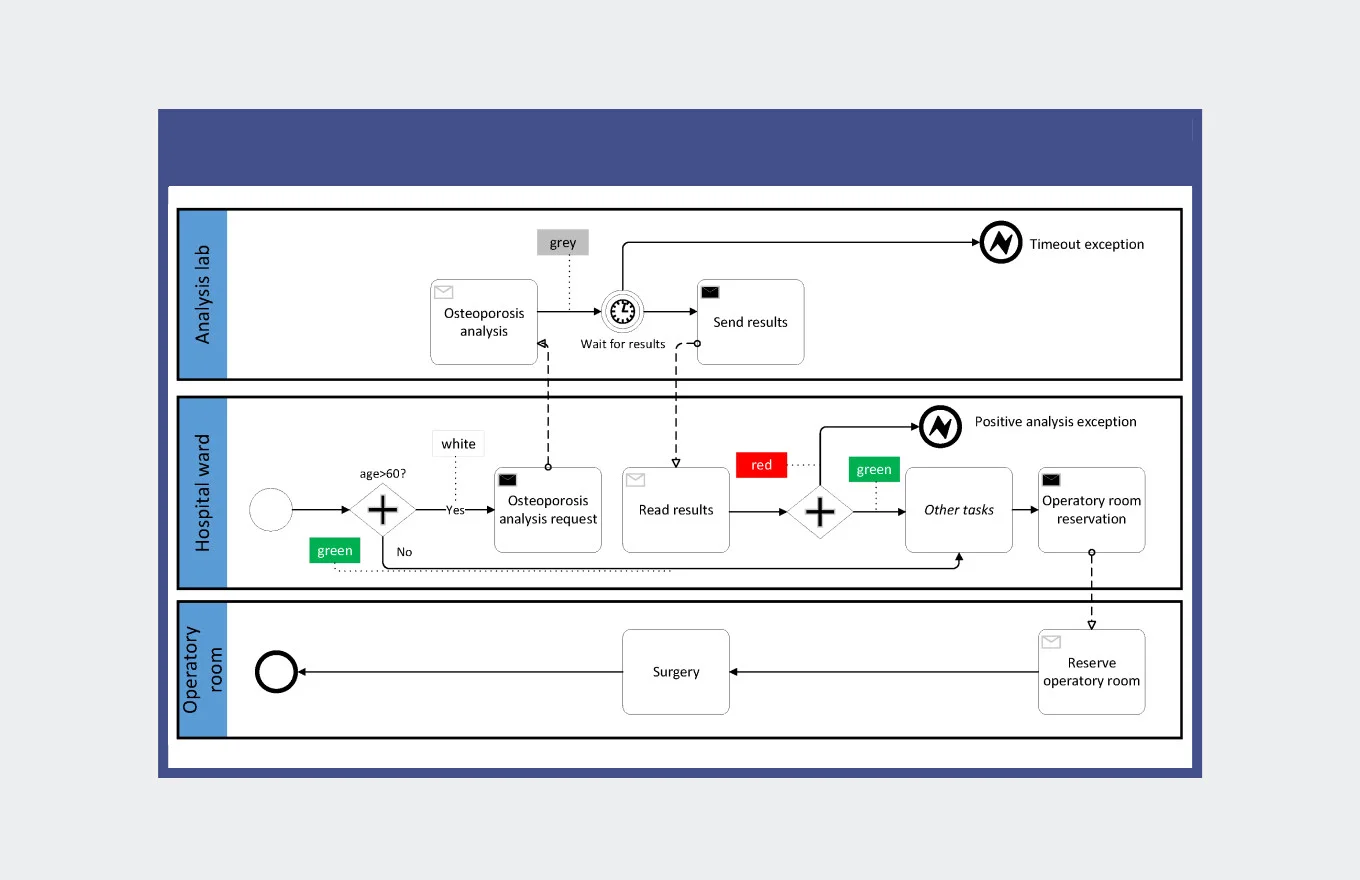
Besides BPMN, you can also use Unified Modelling Language (UML). UML is also a standard used for designing process maps or laboratory workflow charts, including actions, activities, points of decisions, functions, inputs and outputs, stakeholders, measurements of the process, and required time.
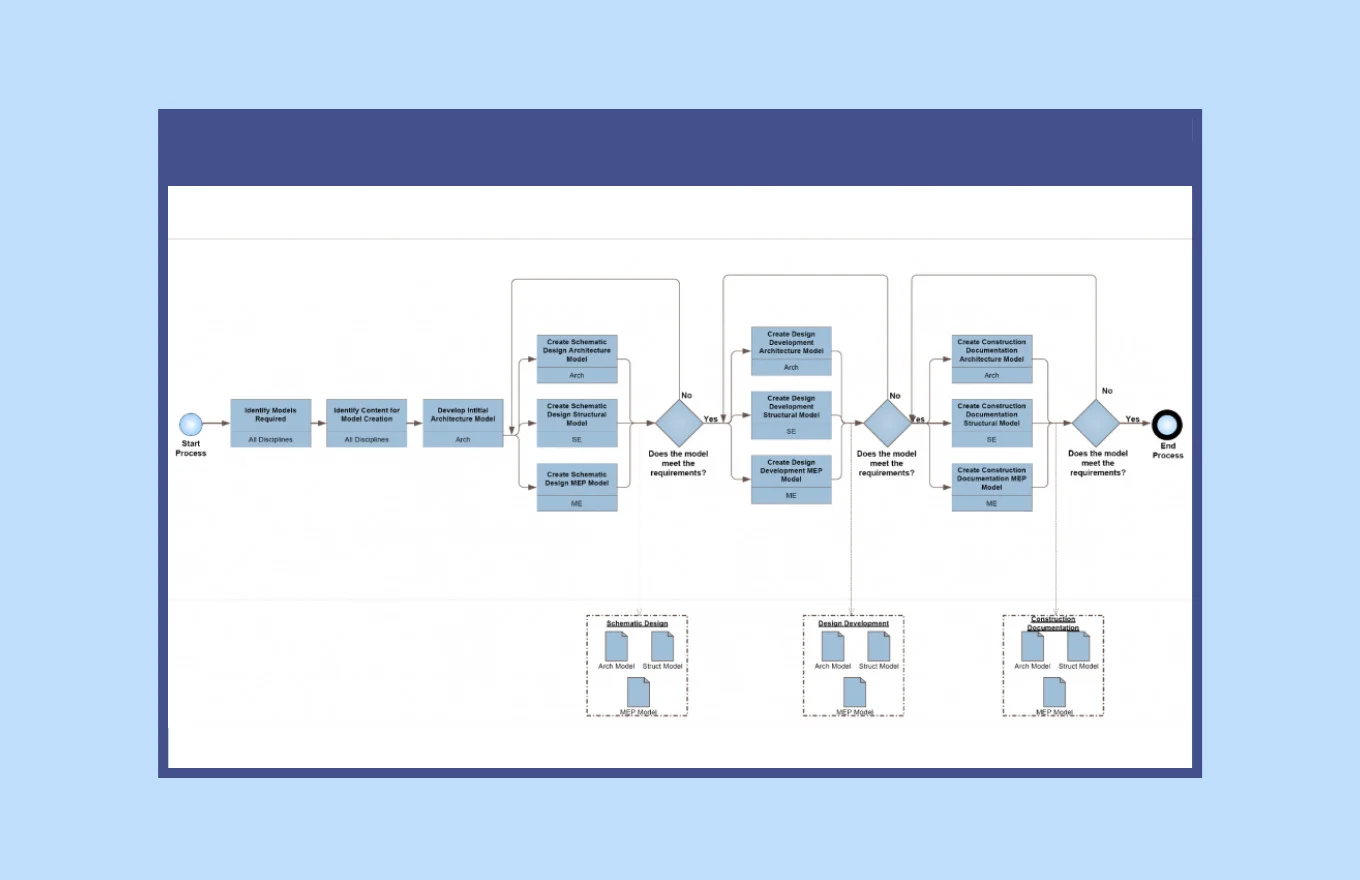
And if you want to implement these standards the right way, use the corresponding software.
When developing a process map, you can apply software from this list:
- LucidChard (free and paid)
- net (free)
- Microsoft Visio (paid)
- Smartsheet (paid with a free trial)
- Heflo (free and paid)
Summary
You cannot reach the full potential of your laboratory without a full understanding of your processes.
And if you start digitizing your lab without this knowledge, your digitization initiative will, eventually, fail. There just will be too much inconsistency between your digital solution and your actual lab workflows.
That’s why you should clearly understand how to do a process map. This knowledge allows you to know and visualize your workflows, down to the slightest detail.
And SoftFormance, a company with rich expertise in laboratory management software development, is ready to give you a helping hand.
Reach us out and see how SoftFormance lab consulting specialists will help you understand your lab workflows and take your laboratory management to a new level.
FAQ
It is a process of mapping out your lab processes aimed at getting a detailed picture of lab workflows supported with time frames, valuable details, and connections.
A great example of a process map is the SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, Customers) diagram, which shows workflows along with their underlying factors and desired outcomes.
The main purpose of lab process mapping is the ability to clearly visualize your lab processes. It can be later used as a roadmap for laboratory digitization.